In today’s complex healthcare landscape, one essential administrative process that significantly affects both revenue and compliance is provider credentialing.
What Is Provider Credentialing?
Provider credentialing is the process through which medical professionals are verified to ensure they have the necessary qualifications, licenses, training, and experience to provide healthcare services. In medical billing, credentialing is crucial because it directly affects a provider’s ability to receive reimbursement from insurance companies.
Without proper credentialing, even the most skilled healthcare providers may experience claim denials, payment delays, or legal liabilities. This makes following a structured and updated Provider Credentialing Guide indispensable.
Why Is Credentialing Important in Medical Billing?
In medical billing, revenue generation depends heavily on payor reimbursements. Credentialing determines whether or not an insurance company will recognize the provider as an in-network professional eligible for payment. If the credentialing process is mishandled or overlooked, providers risk operating out-of-network, which can lead to:
- Rejected claims
- Lower reimbursement rates
- Patient dissatisfaction
- Legal complications
By following a comprehensive Provider Credentialing Guide, medical practices can streamline their revenue cycle and avoid these financial pitfalls.
Steps in the Provider Credentialing Process
A typical credentialing process includes several stages that must be carefully executed. Below is a detailed walkthrough:
Are you missing out on payments due to outdated billing or credentialing processes?
1. Pre-Application Preparation
Before submitting any applications, providers must gather essential documents. These typically include:
- State medical licenses
- DEA registration
- Board certifications
- Malpractice insurance
- Work history and references
A reliable Provider Credentialing Guide should emphasize document accuracy and completeness, as errors can result in significant delays.
2. Application Submission
After compiling the required documents, providers must submit applications to individual insurance companies and credentialing bodies. Each payor has unique requirements, so using a checklist tailored to each plan is crucial. Submission can be done through online portals like CAQH (Council for Affordable Quality Healthcare), which streamlines the process for multiple payors.
3. Primary Source Verification
At this stage, insurance companies perform primary source verification, meaning they check credentials directly with issuing institutions. This step is critical in determining the authenticity of the provider’s qualifications and can take several weeks.
4. Payor Enrollment
Once credentialing is successful, the provider is enrolled with the payor. This enrollment grants the provider an NPI (National Provider Identifier) link with the insurance network and allows them to bill for services.
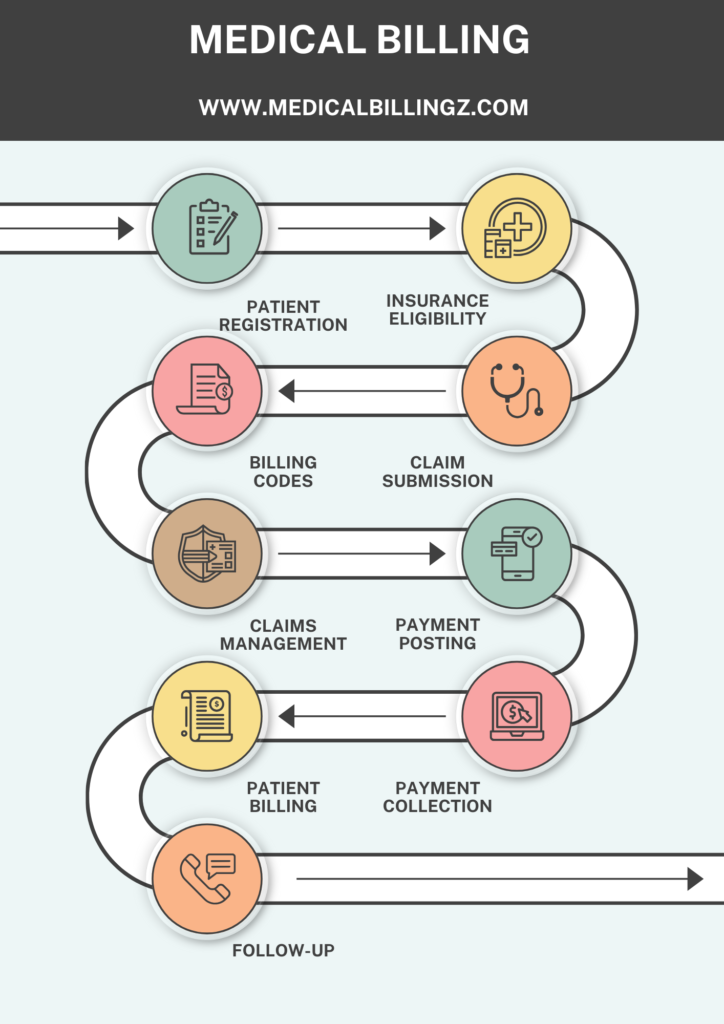
5. Re-Credentialing and Updates
Credentialing is not a one-time process. Most payors require re-credentialing every 2–3 years. Providers must stay updated with license renewals, continuing education, and malpractice coverage to remain compliant.
Key Challenges in Provider Credentialing
Despite its importance, the credentialing process is often plagued with challenges that can create operational bottlenecks. Some common issues include:
- Incomplete or outdated documentation
- Miscommunication between providers and billing staff
- Varied timelines across payors
- Lack of a centralized credentialing system
- Frequent regulation updates
This Provider Credentialing Guide recommends assigning a dedicated credentialing specialist or using software to track timelines and alerts.
Role of Credentialing in Revenue Cycle Management
Credentialing sits at the foundation of revenue cycle management (RCM). A single delay or error in this process can lead to months of denied payments and write-offs. Integrating credentialing seamlessly into the billing workflow ensures:
- Faster claim approvals
- Shorter accounts receivable cycles
- Improved cash flow
- Higher patient retention through in-network status
A strong Provider Credentialing Guide should tie these elements together to support long-term financial stability.
Credentialing vs. Enrollment: Know the Difference
Though often used interchangeably, credentialing and enrollment are distinct processes.
| Credentialing | Enrollment |
|---|---|
| Verifies provider qualifications | Registers provider with payors |
| Involves background checks | Enables billing under specific plans |
| Conducted by payors or third parties | Required for network participation |
| Includes license and certification validation | Links provider to group practices |
| Mandatory before billing begins | Critical for reimbursement |
| Part of compliance protocols | Part of revenue strategy |
Understanding this distinction is essential in implementing an accurate Provider Credentialing Guide for any healthcare practice.
Tips for Streamlining the Credentialing Process
A disorganized credentialing process can hinder practice efficiency. Below are practical tips to improve your workflow:
Use Credentialing Software
Automated platforms can help manage deadlines, update documentation, and minimize human error. These tools often come with built-in reminders and status dashboards.
Keep a Centralized Document Repository
Storing all documents in one secure, cloud-based location makes it easier to submit applications and updates when needed.
Could your practice benefit from automating parts of the medical billing process?
Verify Requirements Early
Every insurance company has different credentialing requirements. Confirm these early in the process to avoid repetitive submissions.
Stay Ahead of Expiry Dates
Use alerts or calendars to track license expirations, DEA renewals, and re-credentialing timelines. Proactive management avoids lapses that could disrupt billing.
Train Staff on Credentialing Basics
All administrative and billing personnel should understand credentialing fundamentals. A shared understanding boosts efficiency and accuracy.
This Provider Credentialing Guide encourages practices to treat credentialing as a continuous and strategic process rather than a one-time task.
Credentialing Timelines and Delays
The average credentialing process can take between 60 to 120 days, depending on the payor, completeness of documentation, and response times from verification sources. Delays often stem from:
- Incorrect data entries
- Missing malpractice insurance proofs
- Delayed responses from licensing boards
- Payor backlogs
A proactive Provider Credentialing Guide should include contingency plans and alternative coverage options to handle such delays, especially for newly hired providers.
Credentialing for Group vs. Individual Providers
Credentialing varies based on the type of provider:
- Individual Providers: Must complete credentialing and enrollment with each payor they wish to bill.
- Group Practices: Must ensure each provider within the group is individually credentialed and linked to the group’s tax ID/NPI.
Your Provider Credentialing Guide must differentiate between these formats to ensure correct and timely billing setup.

Compliance and Legal Considerations
Credentialing is not just an administrative hurdle; it also serves a legal and regulatory purpose. Failure to credential appropriately can lead to:
- Violations of state and federal healthcare laws
- Fines from insurance audits
- Breach of payer contracts
- Malpractice exposure
Following an updated Provider Credentialing Guide ensures your organization meets HIPAA, Medicare, and Medicaid compliance standards.
Conclusion
A robust Provider Credentialing Guide is essential to streamline operations, avoid revenue loss, and maintain compliance in today’s evolving healthcare environment. Credentialing may seem tedious, but its impact on billing efficiency, patient satisfaction, and organizational credibility cannot be overstated. Whether you’re managing a large group practice or launching a solo practice, understanding and implementing credentialing best practices is non-negotiable for long-term success.
Take proactive steps today—use this Provider Credentialing Guide as your foundation to build a seamless, efficient, and error-free credentialing workflow.
FAQs
How long does the provider credentialing process take?
The credentialing process typically takes between 60 to 120 days, depending on the insurance payor, the completeness of submitted documentation, and the responsiveness of licensing boards.
What documents are required for provider credentialing?
Common documents include a valid medical license, DEA certificate, board certifications, malpractice insurance, work history, references, and a completed CAQH profile.
What’s the difference between credentialing and enrollment?
Credentialing verifies the provider’s qualifications, while enrollment links the provider to specific insurance companies, allowing them to bill and receive payments.
Who is responsible for provider credentialing in a medical practice?
Typically, credentialing is handled by administrative staff, billing specialists, or third-party credentialing services, depending on the size and structure of the practice.

