1. Introduction: Why Denials Are a Major Challenge in Medical Billing
Denials remain one of the biggest obstacles in medical billing. Every denied claim leads to revenue loss, administrative workload, and patient dissatisfaction. When denials are frequent, healthcare providers struggle with cash flow, delayed payments, and operational inefficiencies. Some denials arise from clerical mistakes, but many occur because of unfair medical billing practices, such as excessive rejections, hidden payer rules, or inconsistent adjudication.
Minimizing denials requires healthcare providers to understand medical claims billing process, adopt efficient billing practices, and leverage technology. This article provides an in-depth look at the medical claims process, reasons for denials, and strategies to streamline revenue cycle management.
2. What is Claim Processing in Healthcare?
Definition and Importance of Claim Processing
Claim processing in healthcare refers to the systematic submission, adjudication, and settlement of medical claims between providers and payers. It ensures providers are reimbursed for services rendered while giving patients transparency on their financial responsibilities.
Efficient claim processing reduces administrative delays, prevents denials, and strengthens the overall financial health of medical practices.
How Claim Processing Impacts Revenue Cycle Management
The revenue cycle in healthcare begins when a patient schedules an appointment and ends when all payments are received. Claim processing lies at the center of this cycle. Errors or inefficiencies in processing can disrupt revenue, extend accounts receivable (AR) days, and weaken cash flow. Consistent accuracy ensures timely reimbursements, fewer appeals, and a healthier bottom line.

3. Types of Claim Submission in Medical Billing
Electronic Claim Submission (EDI): Faster and More Accurate
Electronic claim submission, also known as Electronic Data Interchange (EDI), is now the industry standard. It enables faster processing, reduced errors, and quick feedback from payers. Automation eliminates paperwork, improves accuracy, and reduces claim rejection rates.
Paper Claim Submission: When It’s Still Used and Its Drawbacks
While paper claims are largely outdated, some small practices and specific insurance providers still rely on them. Paper submissions are prone to manual errors, slower processing times, and increased denials. In fact, many unfair medical billing practices occur when paper claims are mishandled, lost, or delayed intentionally.
Looking to improve your practice’s billing efficiency? Understanding key billing principles
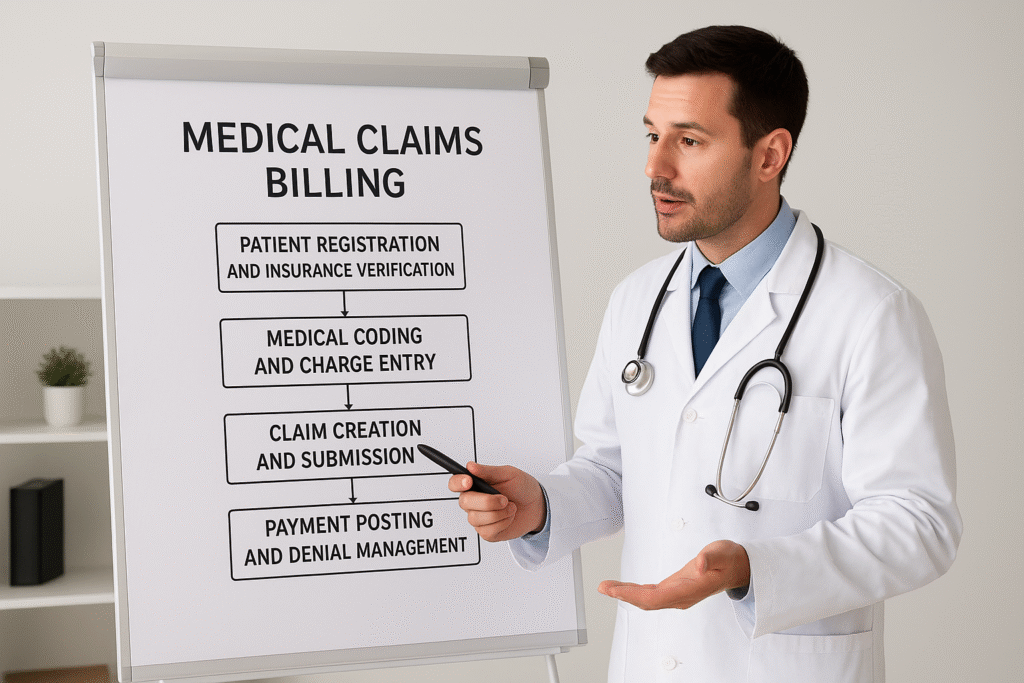
4. The 5-Steps Process
Step 1: Patient Registration and Insurance Verification
Collecting Accurate Demographic Information
Accurate registration is the foundation of clean claim submission. Incorrect names, dates of birth, or insurance IDs result in instant denials.
Importance of Verifying Eligibility and Benefits
Eligibility verification ensures services are covered, reducing the risk of denied claims due to inactive or limited coverage.
Step 2: Medical Coding and Charge Entry
Role of ICD-10, CPT, and HCPCS Codes
Medical coding translates healthcare services into standardized codes. ICD-10, CPT, and HCPCS codes are essential for payer communication.
How Coding Accuracy Prevents Denials
Coding errors remain one of the top denial reasons. Proper training and coding audits prevent costly mistakes.
Step 3: Claim Creation and Submission
Building a Clean Claim: Required Data Elements
A clean claim includes patient demographics, insurance details, provider information, and complete coding.
Submitting Claims via Clearinghouses or Directly to Payers
Clearinghouses act as middlemen, ensuring claims meet payer requirements before submission.
Step 4: Claim Adjudication and Payer Review
What Happens During Payer Adjudication
The payer reviews the claim for accuracy, coverage, and compliance with policies.
Explanation of Benefits (EOB) and Electronic Remittance Advice (ERA)
Providers receive detailed payment or denial reasons through EOBs or ERAs.
Step 5: Payment Posting and Denial Management
Reconciling Payments with Claims
Payments must be matched with claims to ensure accuracy.
Identifying, Appealing, and Preventing Denials
Denials should be tracked, appealed quickly, and analyzed to prevent recurrence.
Top Reasons for Denials and How to Protect Against Unfair Billing Practices
5. Common Reasons Why Medical Claims Get Denied
- Missing or Inaccurate Patient Information – Even minor typos cause claim rejection.
- Coding Errors and Lack of Documentation – Incorrect or missing codes lead to delays.
- Eligibility Issues and Authorization Failures – Services not covered or pre-authorizations not obtained.
- Duplicate Claims or Late Submissions – Resubmitted claims often get denied as duplicates.
Some of these denials are preventable, but others result from unfair medical billing practices by insurers who reject claims despite compliance.
6. Best Practices to Avoid Denials in the Billing Process
Regular Staff Training and Coding Updates
Keeping staff trained on new ICD-10 or CPT updates reduces coding mistakes.
Using Billing Software and Automation Tools
Modern billing software checks claims for errors before submission, preventing unnecessary denials.
Conducting Pre-Submission Claim Audits
Audits ensure all claims meet payer requirements before submission, reducing rejections.
Establishing a Denial Management Strategy
A proactive denial management system tracks patterns, categorizes denials, and implements corrective actions.
7. The Role of Technology in Modern Claims Billing
Benefits of Electronic Health Records (EHR) Integration
EHR integration reduces duplication of data entry, ensuring accuracy and consistency.
AI and Automation in Reducing Errors and Denials
Artificial Intelligence (AI) detects potential errors, predicts denial risks, and automates coding.
Choosing the Right Billing Software for Your Practice
The right solution should include claim scrubbing, eligibility verification, and denial tracking. Reliable software minimizes unfair medical billing practices by enforcing compliance and transparency.
9.Claims Billing Software
| Software Feature | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Claim Scrubbing Tools | Prevents coding errors |
| Eligibility Verification | Reduces coverage denials |
| EHR Integration | Streamlines documentation |
| Automated Denial Tracking | Speeds up appeals |
| Reporting & Analytics | Improves financial insights |
| Cloud-Based Access | Enhances flexibility |
Popular Billing Software
Kareo
A cloud-based platform ideal for small to mid-sized practices. Kareo offers intuitive claim tracking, integrated scheduling, real-time insurance eligibility verification, denial management, billing analytics, and EHR integration.
AdvancedMD
A comprehensive, highly customizable option suited for growing or larger practices. AdvancedMD delivers powerful analytics, claim scrubbing (e.g., ClaimInspector), compliance tracking, billing dashboards, and seamless EHR integration.
DrChrono
A mobile- and cloud-first solution, great for tech-savvy and outpatient providers. DrChrono includes EHR and billing integration, real-time eligibility checks, customizable billing rules, denial analysis, and strong support for Apple devices.
AthenaCollector / athenaOne (Athenahealth)
Part of the athenaOne suite, AthenaCollector focuses on revenue cycle management. It’s known for payer-rule automation, fast reimbursements, strong reporting, patient engagement tools, and integrated billing with clinical workflows.
NextGen Healthcare
Designed for medium to large practices in need of scalability. NextGen offers specialty-specific templates, advanced analytics, strong RCM tools, EHR integration, and automated billing workflows
8. Conclusion: Streamlining the Billing Process for Better Results
Medical billing is a complex yet critical component of healthcare revenue management. From patient registration to denial management, every step affects efficiency, reimbursement, and patient trust. By adopting automation, training staff, and preventing unfair medical billing practices, providers can reduce denials, strengthen financial outcomes, and focus more on patient care.
FAQs
What role does technology play in claim processing?
Technology such as EHR systems, AI-driven coding tools, and billing software reduces manual errors, accelerates submissions, and ensures compliance with payer requirements. Automation also helps track and appeal denials more effectively.
What is the difference between electronic and paper claim submission?
Electronic submissions (EDI) are faster, more accurate, and reduce rejection rates, while paper submissions are slower, error-prone, and still used only in limited cases.
Which medical billing software is best for small practices?
Kareo, DrChrono, and PracticeSuite are excellent options for smaller practices due to their ease of use, affordability, and integrated features. Larger practices may prefer AdvancedMD, NextGen, or AthenaCollector.
How does denial management improve revenue cycle management?
A strong denial management strategy helps identify the root causes of denials, appeal rejected claims quickly, and implement corrective measures—ultimately increasing reimbursements and reducing revenue leakage.

